6.1. 任务执行示例
此示例演示以下内容:
-
如何使用
ProcActionsFragment以编程方式在流程开始时创建流程参与者 -
如何使用
ProcActionsFragment将流程变量传递给流程实例 -
如何获取和修改由
ProcActionsFragment创建的标准流程操作(例如,更改“启动流程”按钮标题) -
如何在没有
ProcActionsFragment的情况下以编程方式启动流程 -
每次流程进行一步时如何使用
ActivitiEventListener自动更新processState字段
此示例使用 Task execution - 1 流程模型:
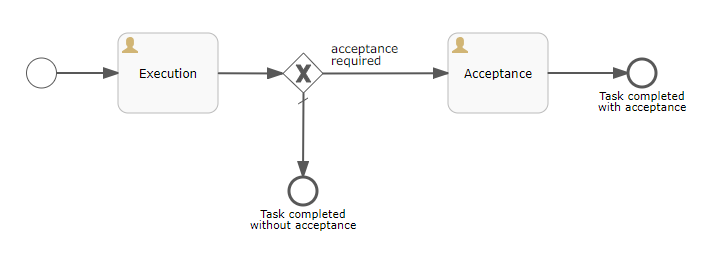
在此示例中,我们不使用 StandardProcForm 来分配流程参与者。我们通过 ProcActionsFragment 的 流程开始前断言 来完成。请参阅 setBeforeStartProcessPredicate() 方法的使用。
@UiController("bpmsamples$Task.edit")
@UiDescriptor("task-edit.xml")
@EditedEntityContainer("taskDc")
@LoadDataBeforeShow
public class TaskEdit extends StandardEditor<Task> {
public static final String PROCESS_CODE = "taskExecution-1";
@Inject
protected ProcActionsFragment procActionsFragment;
@Inject
protected BpmEntitiesService bpmEntitiesService;
@Inject
protected ProcessRuntimeService processRuntimeService;
@Inject
private MessageBundle messageBundle;
@Inject
private Notifications notifications;
@Inject
private Messages messages;
@Inject
private InstanceLoader<Task> taskDl;
...
/** * Method starts the process without {@link ProcActionsFragment} */
@Subscribe("startProcessProgrammaticallyBtn")
private void onStartProcessProgrammaticallyBtnClick(Button.ClickEvent event) {
commitChanges()
.then(() -> {
/*The ProcInstanceDetails object is used for describing a ProcInstance to be created with its proc actors*/
BpmEntitiesService.ProcInstanceDetails procInstanceDetails = new BpmEntitiesService.ProcInstanceDetails(PROCESS_CODE)
.addProcActor("initiator", getEditedEntity().getInitiator())
.addProcActor("executor", getEditedEntity().getExecutor())
.setEntity(getEditedEntity());
/*The created ProcInstance will have two proc actors. None of the entities is persisted yet.*/
ProcInstance procInstance = bpmEntitiesService.createProcInstance(procInstanceDetails);
/*A map with process variables that must be passed to the Activiti process instance when it is started. This variable is used in the model to make a decision for one of gateways.*/
HashMap<String, Object> processVariables = new HashMap<>();
processVariables.put("acceptanceRequired", getEditedEntity().getAcceptanceRequired());
/*Starts the process. The "startProcess" method automatically persists the passed procInstance with its actors*/
processRuntimeService.startProcess(procInstance, "Process started programmatically", processVariables);
notifications.create()
.withCaption(messageBundle.getMessage("processStarted"))
.withType(Notifications.NotificationType.HUMANIZED)
.show();
/*refresh the procActionsFragment to display complete tasks buttons (if a process task appears for the current user after the process is started)*/
initProcActionsFragment();
});
}
private void initProcActionsFragment() {
procActionsFragment.initializer()
.standard()
.setBeforeStartProcessPredicate(() -> {
/*the predicate creates process actors and sets them to the process instance created by the ProcActionsFragment*/
if (commitChanges().getStatus() == OperationResult.Status.SUCCESS) {
ProcInstance procInstance = procActionsFragment.getProcInstance();
ProcActor initiatorProcActor = createProcActor("initiator", procInstance, getEditedEntity().getInitiator());
ProcActor executorProcActor = createProcActor("executor", procInstance, getEditedEntity().getExecutor());
Set<ProcActor> procActors = new HashSet<>();
procActors.add(initiatorProcActor);
procActors.add(executorProcActor);
procInstance.setProcActors(procActors);
return true;
}
return false;
})
.setStartProcessActionProcessVariablesSupplier(() -> {
/*the supplier returns a map with process variables that will be used by the Activiti process*/
Map<String, Object> processVariables = new HashMap<>();
processVariables.put("acceptanceRequired", getEditedEntity().getAcceptanceRequired());
return processVariables;
})
.setAfterStartProcessListener(() -> {
/*custom listener in addition to the standard behavior refreshes the "taskDs", because the process automatically updates the "processState" field of the "Task" entity.*/
notifications.create()
.withCaption(messages.getMessage(ProcActionsFragment.class,"processStarted"))
.withType(Notifications.NotificationType.HUMANIZED)
.show();
initProcActionsFragment();
taskDl.setEntityId(getEditedEntity().getId());
taskDl.load();
})
.setAfterCompleteTaskListener(() -> {
notifications.create()
.withCaption(messages.getMessage(ProcActionsFragment.class,"taskCompleted"))
.withType(Notifications.NotificationType.HUMANIZED)
.show();
initProcActionsFragment();
taskDl.setEntityId(getEditedEntity().getId());
taskDl.load();
})
.init(PROCESS_CODE, getEditedEntity());
}
/** * Method demonstrates how to get and modify process actions automatically created by the ProcActionsFragment */
private void changeStartProcessBtnCaption() {
StartProcessAction startProcessAction = procActionsFragment.getStartProcessAction();
if (startProcessAction != null) {
startProcessAction.setCaption("Start process using ProcActionsFragment");
}
}
}请参阅 TaskEdit.java 中的 setStartProcessActionProcessVariablesSupplier() 方法的用法,作为如何在流程启动时使用 ProcActionsFragment 传递流程变量的示例。其中一个流程网关中使用 acceptanceRequired 变量决定是否必须由发起者接受任务,或者流程必须完成。
changeStartProcessBtnCaption() 演示了如何获取和修改 ProcActionsFragment 生成的流程操作。在此方法中,标准按钮标题“启动流程”将由自定义标题替换。
onStartProcessProgrammaticallyBtnClick() 方法演示了如何在没有 ProcActionsFragment 的情况下启动新的流程实例。
UpdateProcessStateListener.java 是 org.activiti.engine.delegate.event.ActivitiEventListener 的一个实现。此监听器作为流程级别监听器被注册。它执行以下操作:每次到达新的流程步骤时,相关的 com.company.bpmsamples.entity.Task 实体的 processState 字段将使用当前流程步骤名称进行更新。
/** * The listener updates the "processState" field of the {@link HasProcessState} with the name of current BPM process * node. This listener is used in the "taskExecution-1" BPM process */
public class UpdateProcessStateListener implements ActivitiEventListener {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UpdateProcessStateListener.class);
private Metadata metadata;
public UpdateProcessStateListener() {
metadata = AppBeans.get(Metadata.class);
}
@Override
public void onEvent(ActivitiEvent event) {
RuntimeService runtimeService = event.getEngineServices().getRuntimeService();
String executionId = event.getExecutionId();
UUID entityId = (UUID) runtimeService.getVariable(executionId, "entityId");
String entityName = (String) runtimeService.getVariable(executionId, "entityName");
if (entityId == null) {
log.error("Cannot update process state. entityId variable is null");
return;
}
if (Strings.isNullOrEmpty(entityName)) {
log.error("Cannot update process state. entityName variable is null");
return;
}
MetaClass metaClass = metadata.getClass(entityName);
if (metaClass == null) {
log.error("Cannot update process state. MetaClass {} not found", entityName);
return;
}
if (!HasProcessState.class.isAssignableFrom(metaClass.getJavaClass())) {
log.error("{} doesn't implement the HasProcessState");
return;
}
switch (event.getType()) {
case ACTIVITY_STARTED:
//activityName is the name of the current element taken from the process model
String activityName = ((ActivitiActivityEvent) event).getActivityName();
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(activityName)) {
updateProcessState(metaClass, entityId, activityName);
}
break;
}
}
/** * Method updates the process state of the entity linked with the process instance */
private void updateProcessState(MetaClass metaClass, UUID entityId, String processState) {
Persistence persistence = AppBeans.get(Persistence.class);
try (Transaction tx = persistence.getTransaction()) {
EntityManager em = persistence.getEntityManager();
Entity entity = em.find(metaClass.getJavaClass(), entityId);
if (entity != null) {
((HasProcessState) entity).setProcessState(processState);
} else {
log.error("Entity {} with id {} not found", metaClass.getName(), entityId);
}
tx.commit();
}
}
@Override
public boolean isFailOnException() {
return false;
}
}这是流程模型中流程级事件监听器配置界面。

要打开此窗口,请单击建模器中的某个位置,单击 Show advanced properties 链接,然后配置 Event listeners 属性。